Celiac Disease Diet: A Guide to Managing Your Symptoms
If you have been diagnosed with celiac disease, it is essential to follow a gluten-free diet. This means eliminating all sources of gluten from your diet, including bread, pasta, cereals, and processed foods that contain wheat, barley, or rye. In this article, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide to managing your celiac disease symptoms through diet.
Why a Gluten-Free Diet is Necessary for Celiac Disease
Gluten is a protein found in many common foods, including bread, pasta, cereals, and baked goods. For people with celiac disease, consuming gluten triggers an immune response that damages the small intestine. This damage can lead to a variety of symptoms, including:
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Joint pain
- Weight loss
Over time, the damage to the small intestine can cause long-term complications, such as malnutrition, osteoporosis, and even certain types of cancer. The only treatment for celiac disease is a gluten-free diet, which eliminates all sources of gluten from the diet.
What Foods to Avoid on a Gluten-Free Diet
When following a gluten-free diet, it is essential to avoid all sources of gluten. Some foods that contain gluten include:
- Wheat
- Barley
- Rye
- Bread
- Pasta
- Cereals
- Crackers
- Cookies
- Cakes
- Pastries
- Beer
It is also important to read food labels carefully, as many processed foods contain hidden sources of gluten. Look for the words "wheat," "barley," or "rye" on the ingredient list, and avoid any foods that contain these ingredients. Some foods that may contain hidden sources of gluten include:
- Soy sauce
- Salad dressings
- Soup mixes
- Gravy
- Seasonings
- Processed meats
- Hot dogs
- Vegetarian meat substitutes
- French fries
Gluten-Free Alternatives
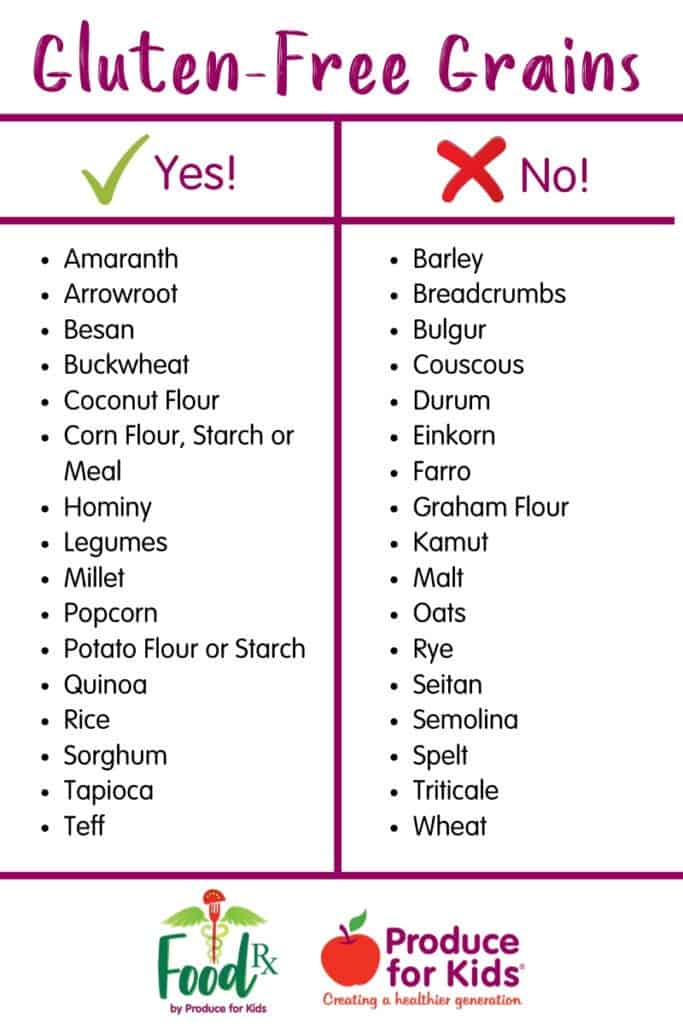
Fortunately, there are many gluten-free alternatives available for people with celiac disease. Some gluten-free grains include:
- Rice
- Corn
- Oats (make sure they are certified gluten-free)
- Quinoa
- Buckwheat
- Millet
Many gluten-free products are now available in grocery stores, including bread, pasta, and baked goods. However, it is important to read labels carefully, as some gluten-free products may still contain small amounts of gluten. Look for products that are certified gluten-free.
Meal Planning for a Gluten-Free Diet
Meal planning is an essential part of managing celiac disease. Here are some tips for planning gluten-free meals:
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and gluten-free grains.
- Plan ahead by creating a weekly meal plan and grocery shopping list.
- Prepare meals at home to ensure that they are gluten-free.
- Avoid eating out unless you can confirm that the restaurant offers gluten-free options.
- Be creative with your cooking and try new recipes that are gluten-free.
Sample Gluten-Free Meal Plan
| Meal | Gluten-Free Option |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Gluten-free oatmeal with fresh berries and almond milk |
| Lunch | Turkey lettuce wraps with avocado and gluten-free crackers |
| Dinner | Grilled chicken with roasted vegetables and quinoa |
| Snack | Apple slices with almond butter |
Benefits and Drawbacks of a Gluten-Free Diet
Benefits
A gluten-free diet can provide many benefits for people with celiac disease, including:
- Improved digestion
- Reduced inflammation in the body
- Increased energy levels
- Better nutrient absorption
- Reduced risk of long-term complications
Drawbacks
However, there are also some drawbacks to a gluten-free diet, including:
- It can be expensive, as gluten-free products are often more expensive than their gluten-containing counterparts.
- It can be difficult to follow, as gluten is found in many common foods.
- It can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not followed properly.
- It can be socially isolating, as it can be challenging to eat out or attend social events where food is served.
FAQs
Q: Can celiac disease be cured?
A: There is currently no cure for celiac disease. The only treatment is a gluten-free diet.
Q: Can people with celiac disease eat oats?
A: Yes, people with celiac disease can eat oats as long as they are certified gluten-free. However, some people with celiac disease may still experience symptoms when consuming oats.
Q: Can people with celiac disease eat wheat-free products?
A: Not necessarily. Wheat-free products may still contain gluten from other sources, such as barley or rye. It is essential to look for products that are certified gluten-free.
Q: Can people with celiac disease consume alcohol?
A: Yes, people with celiac disease can consume alcohol as long as it is gluten-free. Beer and other malt beverages are not gluten-free, but there are many gluten-free alternatives available, such as wine, cider, and spirits.
Conclusion
A gluten-free diet is essential for people with celiac disease to manage their symptoms and prevent long-term complications. By eliminating all sources of gluten from their diet and focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, people with celiac disease can improve their digestion, increase their energy levels, and reduce their risk of complications. While following a gluten-free diet can be challenging, it is possible to enjoy a varied and satisfying diet with proper planning and preparation.
