Abortion Laws in the United States
History of Abortion Laws in the United States
Pre-Roe v. Wade
Before the landmark Supreme Court case Roe v. Wade in 1973, abortion was largely illegal in the United States. However, some states had begun to liberalize their abortion laws in the 1960s, allowing for abortions in certain circumstances such as danger to the mother's life or in cases of rape or incest.
Roe v. Wade
In 1973, the Supreme Court ruled in Roe v. Wade that the right to privacy under the Due Process Clause of the 14th Amendment extended to a woman's decision to have an abortion. This ruling effectively legalized abortion nationwide, although individual states were allowed to regulate or restrict access to abortion in certain ways.
Post-Roe v. Wade
Since the Roe v. Wade decision, there have been numerous attempts to restrict access to abortion through legislation and court cases. Some of these restrictions include waiting periods, mandatory counseling, and parental consent laws. In recent years, there has been a push to ban abortions after a certain point in the pregnancy, such as the controversial "heartbeat bills" that ban abortions after a fetal heartbeat can be detected.
Current State of Abortion Laws in the United States
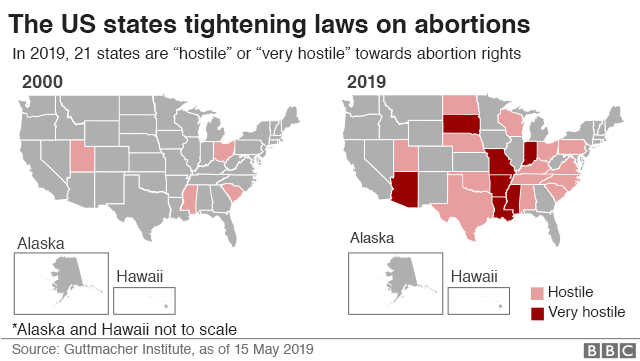
Currently, the legality and availability of abortion varies widely from state to state. Some states have very restrictive laws that make it difficult for women to access abortion, while others have more liberal laws that protect a woman's right to choose.
States with Restrictive Abortion Laws
States with restrictive abortion laws often require waiting periods, mandatory counseling, and parental consent for minors. Some states also have laws that require women to undergo an ultrasound before having an abortion, or that ban abortions after a certain point in the pregnancy.
Texas
Texas is one of the most restrictive states when it comes to abortion laws. In 2013, the state passed a law that required abortion clinics to meet the same standards as ambulatory surgical centers, which led to the closure of many clinics. In 2016, the Supreme Court struck down the law, but the state has continued to pass restrictive abortion laws.
Alabama
Alabama has some of the most restrictive abortion laws in the country. In 2019, the state passed a law that banned abortions in almost all cases, including in cases of rape and incest. The law was blocked by a federal judge, but the state has continued to push for strict abortion restrictions.
States with Liberal Abortion Laws
States with liberal abortion laws often have fewer restrictions on access to abortion. Some states have laws that protect a woman's right to choose, even if Roe v. Wade were to be overturned.
California
California is known for having some of the most liberal abortion laws in the country. The state allows abortions up to 24 weeks, and has no waiting period or mandatory counseling requirements.
New York
New York passed the Reproductive Health Act in 2019, which legalized abortion up to 24 weeks and allowed for abortions after that point if the mother's life is at risk or the fetus is not viable.
Pros and Cons of Abortion Laws
Pros of Liberal Abortion Laws
- Protects a woman's right to choose what happens to her body
- Allows women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health
- Reduces the number of unsafe and illegal abortions
- Allows women to pursue education and career goals without being held back by unintended pregnancies
Cons of Liberal Abortion Laws
- Can be seen as morally wrong and against religious beliefs
- Can lead to an increase in abortions
- Can cause psychological harm to women who have abortions
- Can create conflict and division within communities and families
Pros of Restrictive Abortion Laws
- Protects the rights of the unborn fetus
- Can prevent women from making hasty decisions about their reproductive health
- Can lead to a decrease in abortions
- Can promote adoption as an alternative to abortion
Cons of Restrictive Abortion Laws
- Can be seen as a violation of a woman's right to choose what happens to her body
- Can lead to an increase in unsafe and illegal abortions
- Can prevent women from seeking necessary medical care
- Can disproportionately affect low-income women and women of color
FAQ
Q: What is Roe v. Wade?
A: Roe v. Wade is a landmark Supreme Court case that legalized abortion nationwide in 1973.
Q: Can states ban abortion completely?
A: No, states cannot ban abortion completely due to the Supreme Court's ruling in Roe v. Wade. However, they can regulate and restrict access to abortion in certain ways.
Q: What are "heartbeat bills"?
A: "Heartbeat bills" are laws that ban abortions after a fetal heartbeat can be detected, which is usually around six weeks into the pregnancy.
Q: Are there any states that protect a woman's right to choose even if Roe v. Wade is overturned?
A: Yes, some states have passed laws that protect a woman's right to choose even if Roe v. Wade is overturned, including California and New York.
Conclusion
The issue of abortion laws in the United States is a complex and emotionally charged topic. While some believe that women should have the right to choose what happens to their bodies, others believe that abortion is morally wrong and should be illegal. Regardless of one's personal beliefs, it is important to understand the history and current state of abortion laws in the United States, as well as the pros and cons of each side. Ultimately, the decision of whether to legalize or restrict abortion will continue to be a highly debated issue in the United States.
