State by State Abortion Laws
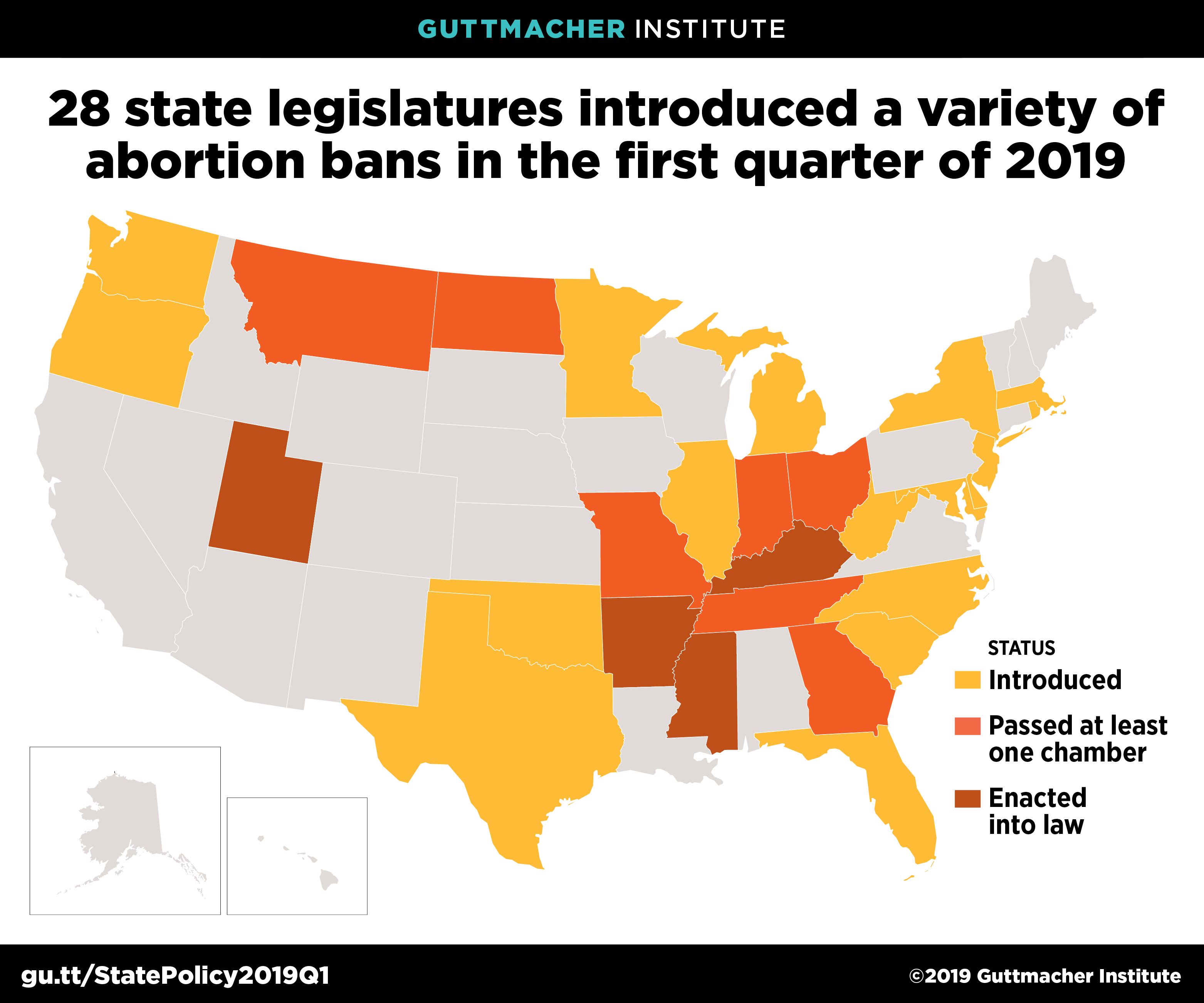
Abortion Laws by State
States with the Most Restrictive Abortion Laws
In recent years, several states have passed highly restrictive abortion laws, often referred to as "heartbeat bills" because they ban abortions after a fetal heartbeat can be detected. These states include:
- Alabama
- Georgia
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Ohio
These laws have faced legal challenges and are currently not in effect in all states.
States with the Least Restrictive Abortion Laws
Other states have passed laws that protect and expand access to abortion. These states include:
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Hawaii
- Oregon
- Washington
These states have laws that ensure access to abortion without unnecessary restrictions and protect a woman's right to choose.
States with Pending Abortion Legislation
Several states have pending legislation that could impact access to abortion. These states include:
- Texas
- Florida
- North Carolina
- Arkansas
- Oklahoma
These states have proposed legislation that could restrict access to abortion or expand current laws.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Abortion laws are complex and often controversial, with supporters and opponents on both sides of the issue. Some argue that restrictive laws protect the rights of the unborn and ensure that women make informed decisions about their bodies. Others argue that these laws limit access to healthcare and infringe upon a woman's right to choose.
On the other hand, laws that protect and expand access to abortion can ensure that women have control over their reproductive health and can make informed decisions about their bodies. However, opponents argue that these laws promote a culture of death and can lead to the loss of innocent life.
FAQs
Q: What is Roe v. Wade?
A: Roe v. Wade is a landmark Supreme Court decision that legalized abortion nationwide in 1973.
Q: Can states ban abortion?
A: While Roe v. Wade legalized abortion nationwide, states can regulate the procedure and enact their own laws regarding abortion.
Q: What are "heartbeat bills"?
A: "Heartbeat bills" are highly restrictive abortion laws that ban abortions after a fetal heartbeat can be detected, which is often around six weeks into a pregnancy.
Q: Do all states have waiting period requirements for abortion?
A: No, not all states require a waiting period before an abortion can be performed.
