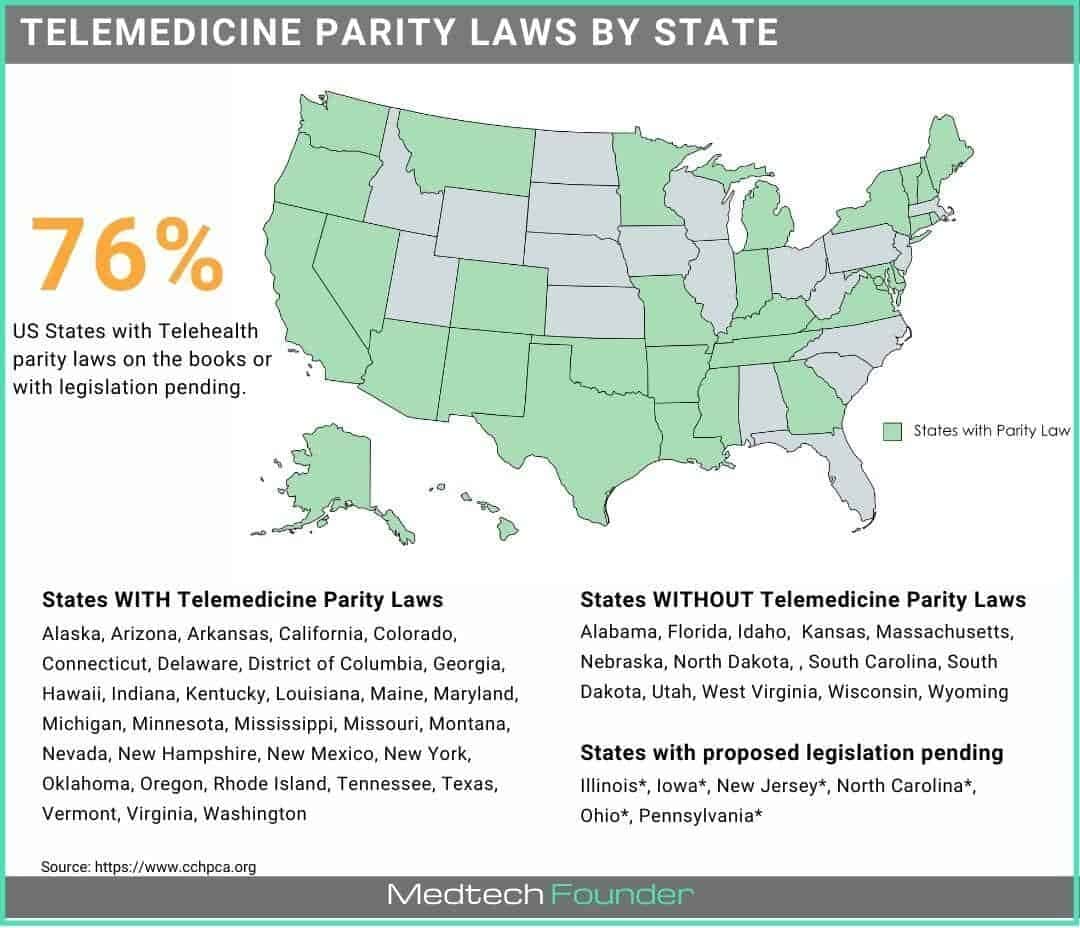
Telehealth Laws by State
What are Telehealth Laws?
Telehealth laws are regulations that govern the use of telehealth services. These laws are set by state governments and vary from state to state. Telehealth laws cover a wide range of topics such as licensure, reimbursement, privacy, and security. It is important for healthcare providers to be aware of the telehealth laws in their state to ensure compliance.
Telehealth Laws by State
Each state has its own set of telehealth laws. Here are some examples:
California
California has one of the most comprehensive telehealth laws in the country. It requires health plans to cover telehealth services to the same extent as in-person services. California also allows out-of-state healthcare providers to provide telehealth services to California residents.
Texas
Texas has a telemedicine law that requires a patient to have an established relationship with a healthcare provider before receiving telehealth services. Texas also requires healthcare providers to have a license to practice medicine in Texas to provide telehealth services to Texas residents.
New York
New York has a telehealth parity law that requires health plans to cover telehealth services to the same extent as in-person services. New York also requires healthcare providers to have a license to practice medicine in New York to provide telehealth services to New York residents.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Telehealth
Advantages
- Increased access to healthcare services
- Convenience for patients who are unable to travel
- Cost-effective for both patients and healthcare providers
- Reduces the risk of exposure to infectious diseases
Disadvantages
- Technical difficulties can hinder the delivery of healthcare services
- Lack of physical examination may result in misdiagnosis
- Privacy and security concerns
- Not all healthcare services can be provided via telehealth
FAQs
Q: Is telehealth covered by insurance?
A: It depends on the state and the insurance plan. Some states have telehealth parity laws that require health plans to cover telehealth services to the same extent as in-person services. However, not all insurance plans cover telehealth services.
Q: Can I receive telehealth services from an out-of-state healthcare provider?
A: It depends on the state. Some states allow out-of-state healthcare providers to provide telehealth services to their residents, while others require healthcare providers to have a license to practice medicine in the state where the patient is located.
Q: What equipment do I need for a telehealth appointment?
A: You will need a device with a camera and microphone, such as a smartphone, tablet, or computer. You will also need an internet connection.
Q: What healthcare services can be provided via telehealth?
A: Many healthcare services can be provided via telehealth, including virtual consultations, mental health services, and remote monitoring of chronic conditions. However, some healthcare services require a physical examination and cannot be provided via telehealth.
