The Law of Conservation of Mass States That: Understanding the Fundamental Principle of Chemistry
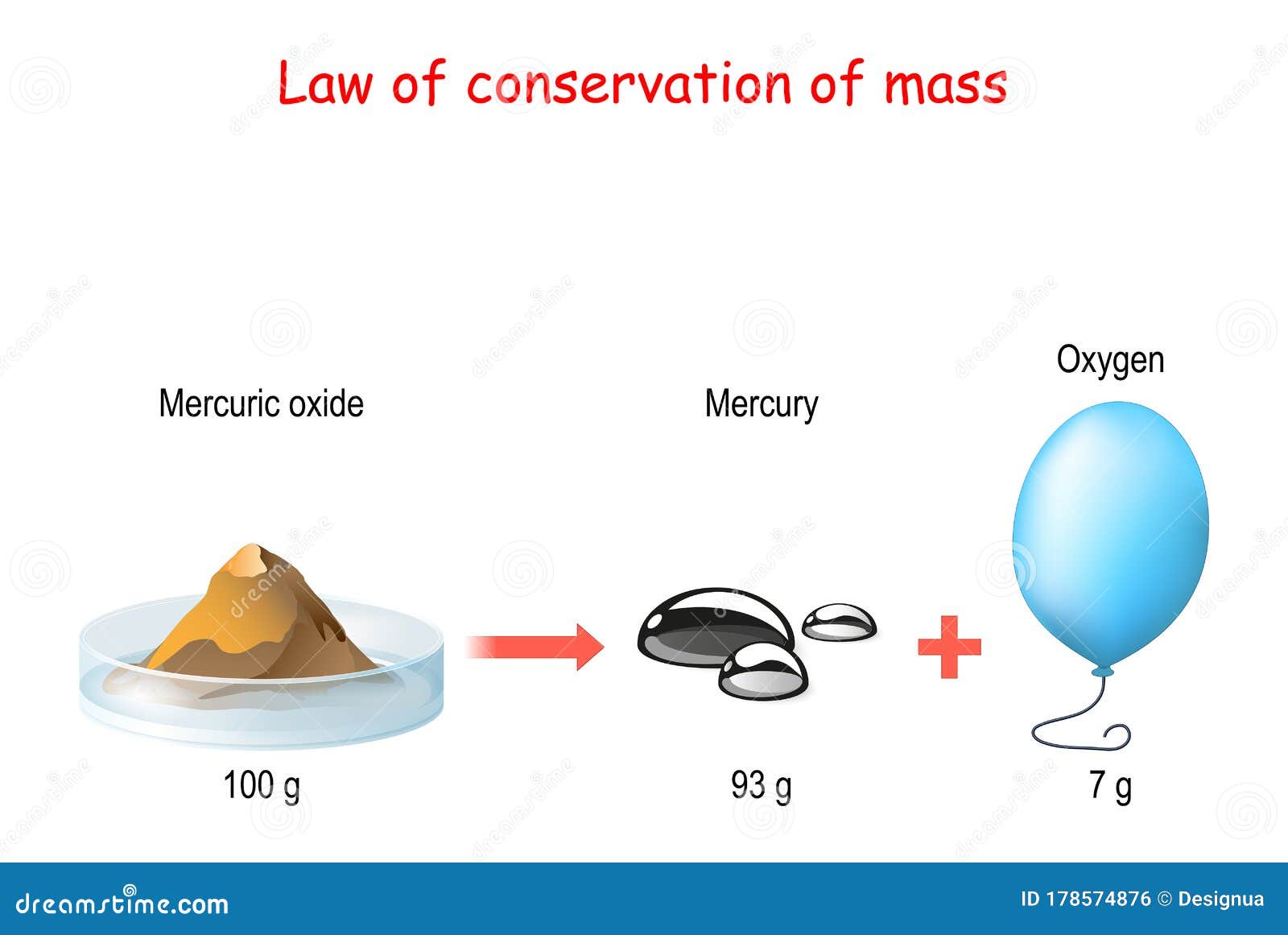
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that the total mass of a closed system remains constant during a chemical reaction. This means that the mass of the reactants before the reaction is equal to the mass of the products after the reaction. In other words, matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
How does the Law of Conservation of Mass work?
The Law of Conservation of Mass works by balancing the chemical equation. This means that the number of atoms of each element in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms of each element in the products. Balancing the chemical equation ensures that the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products.
Why is the Law of Conservation of Mass important?
The Law of Conservation of Mass is important because it is a fundamental principle of chemistry. Understanding this law helps chemists predict the outcome of chemical reactions and design new reactions. It also helps in the development of new technologies and materials.
Expanding the Keyword: The Importance of the Law of Conservation of Mass in Chemistry
The Law of Conservation of Mass is a crucial concept in chemistry and is used to understand and predict the outcome of chemical reactions. It is based on the principle of the conservation of matter, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. The law helps to ensure that chemical reactions are balanced and that the mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products.
The Importance of Balancing Chemical Equations
When balancing a chemical equation, it is essential to ensure that the number of atoms of each element in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms of each element in the products. This ensures that the Law of Conservation of Mass is followed, and the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products.
The Role of the Law of Conservation of Mass in Chemical Reactions
The Law of Conservation of Mass plays a significant role in chemical reactions by ensuring that the mass of the reactants is conserved. This helps chemists predict the outcome of reactions and design new reactions. It also helps in the development of new technologies and materials.
The Relationship between the Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy
The Law of Conservation of Mass is related to the Law of Conservation of Energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. Both laws are fundamental principles of science and are essential in understanding the physical world around us.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of the Law of Conservation of Mass
Advantages
- The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental principle of chemistry and helps chemists predict the outcome of chemical reactions.
- It ensures that chemical reactions are balanced and that the mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products.
- It helps in the development of new technologies and materials.
Disadvantages
- The Law of Conservation of Mass does not take into account the release or absorption of energy during a chemical reaction.
- It assumes that the reaction is occurring in a closed system, which is not always the case in real-world situations.
Conclusion
The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental principle of chemistry that states that the total mass of a closed system remains constant during a chemical reaction. The law helps chemists predict the outcome of reactions and design new reactions. It is also essential in the development of new technologies and materials. However, it has its limitations, such as not taking into account the release or absorption of energy during a chemical reaction.
FAQs
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?
The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental principle of chemistry that states that the total mass of a closed system remains constant during a chemical reaction. This means that the mass of the reactants before the reaction is equal to the mass of the products after the reaction.
Who discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass?
The Law of Conservation of Mass was first discovered by Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18th century.
What is the role of the Law of Conservation of Mass in chemical reactions?
The Law of Conservation of Mass ensures that the mass of the reactants is conserved during a chemical reaction. It helps chemists predict the outcome of reactions and design new reactions. It is also essential in the development of new technologies and materials.
What are the limitations of the Law of Conservation of Mass?
The Law of Conservation of Mass does not take into account the release or absorption of energy during a chemical reaction. It also assumes that the reaction is occurring in a closed system, which is not always the case in real-world situations.
