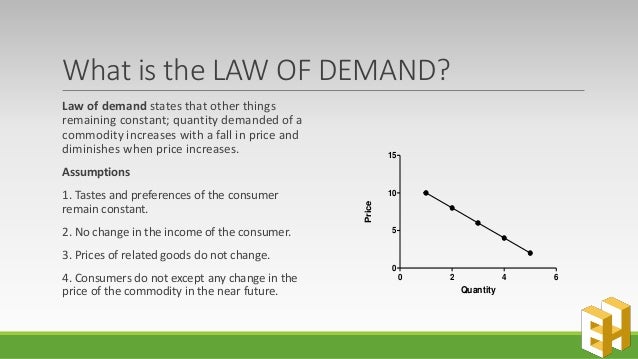
The Law of Demand States That
How Does the Law of Demand Work?
The law of demand is based on the principle of utility, which states that consumers will always seek to maximize their total utility or satisfaction from the goods and services they consume. As a result, consumers will buy more of a good or service when its price is low and less of it when its price is high. This inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded is what creates the downward-sloping demand curve.
Factors That Affect Demand
While price is the most important factor that affects demand, there are other factors that can also have an impact, including:
1. Income
As consumers' income increases, their ability to purchase goods and services also increases. This can lead to an increase in demand for some goods and services.
2. Prices of Related Goods
The prices of substitute and complementary goods can also affect demand. Substitute goods are those that can be used in place of another good, while complementary goods are those that are used together with another good. For example, if the price of coffee increases, the demand for tea (a substitute good) may increase, while the demand for sugar (a complementary good) may decrease.
3. Tastes and Preferences
Consumers' tastes and preferences can also affect demand. If a good or service becomes more popular or trendy, demand for it may increase, even if its price remains the same.
4. Future Expectations
Consumers' expectations about future prices or availability of a good or service can also affect demand. If consumers expect the price of a good to increase or the supply to decrease in the future, they may buy more of it now, even if its price is currently high.
The Demand Curve
The demand curve is a graphical representation of the law of demand. It shows the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded of that good or service. The demand curve is downward-sloping, which means that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded of that good or service will decrease.
The demand curve can shift to the left or right depending on changes in factors other than price that affect demand. When the demand curve shifts to the left, it means that consumers are willing to buy less of a good or service at every price level. When the demand curve shifts to the right, it means that consumers are willing to buy more of a good or service at every price level.
Advantages
- The law of demand is a fundamental principle of economics that helps explain how consumers make purchasing decisions.
- Understanding the law of demand can help businesses determine the optimal pricing strategy for their products or services.
- The law of demand is supported by empirical evidence and has been validated by numerous studies.
Disadvantages
- The law of demand assumes that all other factors affecting demand remain constant, which may not always be the case in the real world.
- The law of demand does not account for changes in consumer behavior due to external factors such as advertising or changes in social norms.
- The law of demand assumes that consumers are rational and always seek to maximize their utility, which may not always be true in practice.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between a change in quantity demanded and a change in demand?
A1. A change in quantity demanded is a movement along the demand curve in response to a change in price, while a change in demand is a shift of the entire demand curve due to a change in one or more of the factors that affect demand.
Q2. How does the law of demand relate to elasticity?
A2. The elasticity of demand measures how responsive consumers are to changes in price. When demand is elastic, a small change in price will lead to a large change in quantity demanded. When demand is inelastic, a change in price will have little effect on quantity demanded. The law of demand assumes that demand is always downward-sloping and therefore elastic.
Q3. Is the law of demand applicable to all goods and services?
A3. The law of demand is generally applicable to most goods and services, but there are exceptions. For example, some luxury goods may actually see an increase in demand as their price increases, as consumers perceive them as more exclusive and desirable.
Q4. Can the law of demand be used to predict consumer behavior?
A4. The law of demand provides a basic framework for understanding how consumers respond to changes in price, but it cannot be used to predict consumer behavior with 100% accuracy. Consumer behavior is influenced by a wide range of factors, and the law of demand is just one of many tools that businesses can use to make informed decisions.
