What Does Law of Demand State?
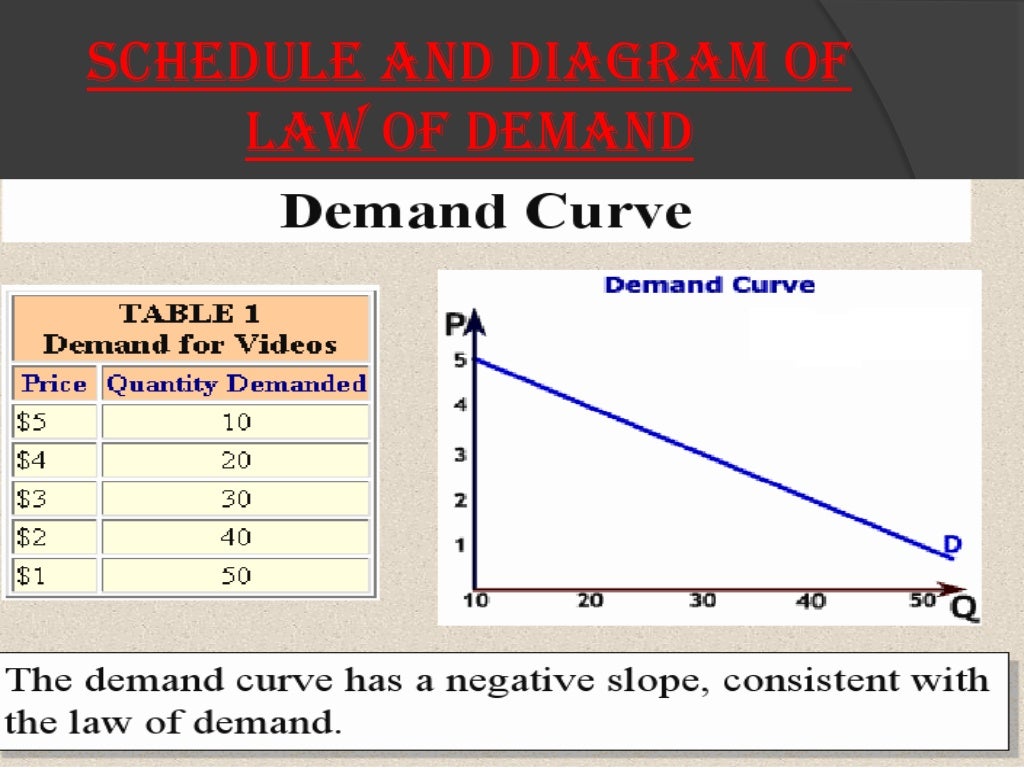
What is the Law of Demand?
The law of demand is a basic economic principle that explains how the quantity of a product or service demanded by consumers changes in response to changes in its price. According to the law of demand, as the price of a product or service increases, the demand for that product or service will decrease, and vice versa.
How Does the Law of Demand Work?
The law of demand works by assuming that all other factors that affect demand, such as income and consumer preferences, are held constant. When the price of a product or service increases, consumers will typically purchase less of that product or service because they can find cheaper alternatives or simply because they cannot afford it. Conversely, when the price of a product or service decreases, consumers will typically purchase more of that product or service because it becomes more affordable.
What Are the Key Factors that Affect Demand?
There are several key factors that affect demand, including:
- Price of the product or service
- Income of consumers
- Consumer preferences
- Availability of substitutes
- Marketing and advertising
Advantages of the Law of Demand
The law of demand provides several advantages, including:
- It helps businesses to set prices for their products or services
- It helps consumers to make informed purchasing decisions
- It provides a basic framework for analyzing market trends and consumer behavior
Disadvantages of the Law of Demand
Despite its advantages, the law of demand has some limitations, including:
- It assumes that all other factors that affect demand are held constant, which is rarely the case in the real world
- It does not account for situations where consumers may purchase more of a product or service at higher prices (such as luxury goods)
- It does not account for situations where consumers may purchase less of a product or service at lower prices (such as products with negative social stigma)
Conclusion
The law of demand is a fundamental concept in economics that explains how the price of a product or service affects the quantity of that product or service demanded by consumers. While it has some limitations, it provides a useful framework for analyzing market trends and consumer behavior. By understanding the law of demand, businesses can set prices for their products or services that are more in line with consumer demand, and consumers can make more informed purchasing decisions.
FAQ
Q: Does the law of demand apply to all products and services?
A: Yes, the law of demand applies to all products and services, regardless of their nature or type.
Q: Is the law of demand always accurate?
A: No, the law of demand is not always accurate because it assumes that all other factors that affect demand remain constant, which is rarely the case in the real world.
Q: Can the law of demand be used to predict consumer behavior?
A: Yes, the law of demand provides a basic framework for predicting consumer behavior and analyzing market trends.
Q: What is the difference between demand and quantity demanded?
A: Demand refers to the entire relationship between the price of a product or service and the quantity of that product or service demanded by consumers, while quantity demanded refers to a specific quantity of a product or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price.
