What Does the Law of Supply State?
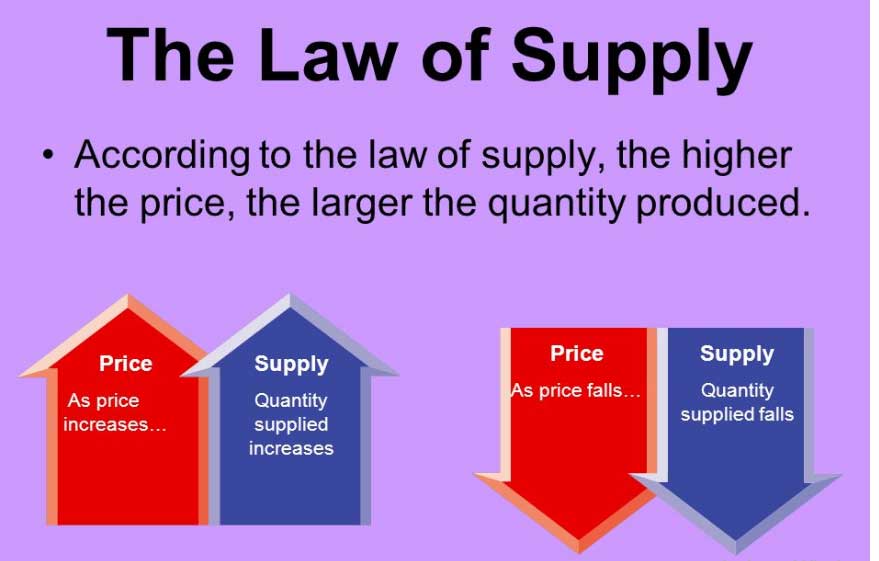
How Does the Law of Supply Work?
According to the law of supply, when the price of a good increases, suppliers will want to produce more of it because they can earn a higher profit. For example, if the price of apples increases, apple farmers will want to produce more apples in order to take advantage of the higher price.
On the other hand, if the price of a good decreases, suppliers will want to produce less of it because it becomes less profitable. For example, if the price of apples decreases, apple farmers may decide to switch to producing a different crop that is more profitable.
Therefore, the quantity of a good supplied is directly related to its price. As the price of a good increases, the quantity supplied also increases, and vice versa.
Factors Affecting the Law of Supply
While the law of supply may seem straightforward, there are several factors that can affect how much of a good suppliers are willing to produce and sell:
- The cost of production: If the cost of producing a good increases, suppliers may be less willing to produce and sell it.
- Technological advancements: New technologies can make production more efficient, which can increase the supply of a good.
- The number of suppliers: When there are more suppliers in the market, the supply of a good is likely to increase.
- The price of related goods: If the price of a substitute good increases, suppliers may switch to producing that good instead.
- Government policies: Taxes, subsidies, and regulations can all affect the supply of a good.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Law of Supply
One advantage of the law of supply is that it helps to ensure that goods are produced efficiently. When prices are high, suppliers are motivated to produce more of a good, which can help to meet demand and prevent shortages. On the other hand, a disadvantage of the law of supply is that it can lead to overproduction and waste. If prices are too high and suppliers produce too much of a good, they may end up with excess inventory that they cannot sell.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between the law of supply and the law of demand?
A: The law of supply states that the quantity of a good supplied increases as its price increases, while the law of demand states that the quantity of a good demanded decreases as its price increases.
Q: How does the law of supply affect the economy?
A: The law of supply helps to ensure that goods are produced efficiently and that prices are determined by market forces rather than government intervention.
Q: What happens when the supply of a good exceeds the demand?
A: When the supply of a good exceeds the demand, prices are likely to fall as suppliers try to sell off their excess inventory.
Q: Can the law of supply be broken?
A: The law of supply is a fundamental principle of economics, but there may be exceptions in certain situations (e.g., if a natural disaster disrupts the supply chain for a particular good).
